Demodox blepharitis treatment shows positive results, says Tarsus
IRVINE— Tarsus Pharmaceuticals announces positive results of its Phase 2a Mars Study and the release of the results of a Phase 2b randomized controlled study.
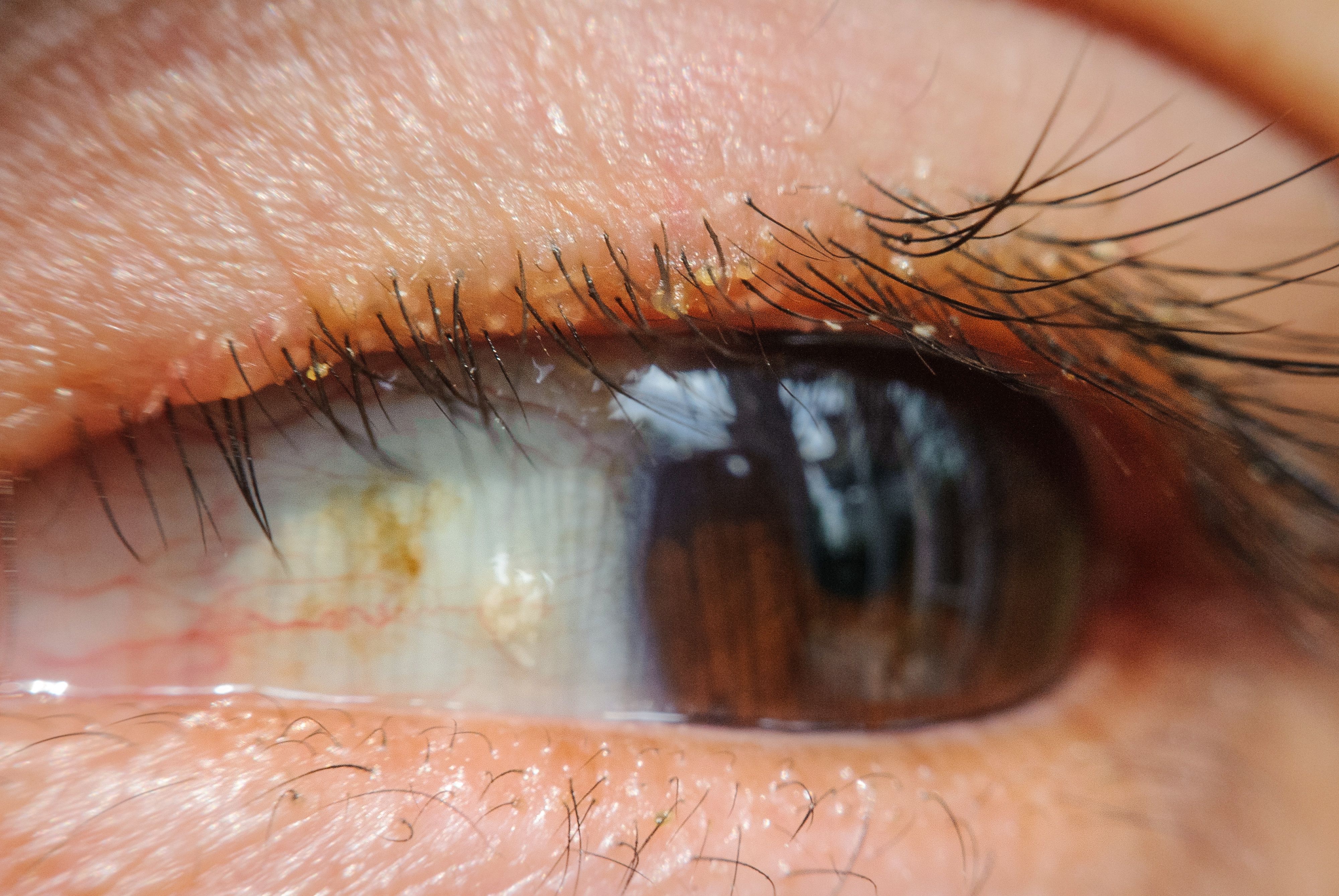
The Mars study demonstrated that the use of TP-03 for 4 weeks was well-tolerated and showed promising efficacy in the treatment of demodex blepharitis with treatment effects persisting for at least 90 days, according to the company.
“My colleagues and I are excited that there is a possible new therapy that targets the underlying cause of disease for nearly half of all blepharitis patients,” says Dr. Roberto Gonzalez-Salinas, MD, PhD, the principal investigator for the study conducted at the Asociación para Evitar la Ceguera in Mexico City.
Study design
Mars was a single-arm, open-label study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of TP-03 in 15 participants with demodex blepharitis. The prespecified efficacy endpoints were improvement in collarette score and mite density. Participants dosed one drop of TP-03 in each eye bid for 28 days.
Results showed statistically significant decreases in mean collarette score and mite density beginning at Day 14 and continuing throughout the study period of 90 days with no adverse events reported, according to the company.
Related: NIH launches clinical trials network: COVID-19 vaccine underway
Specific results were:
• Collarette score: The mean grade showed statistically significant improvement from baseline to Day 14 and had a 2-grade improvement overall on a 4-point scale by the end of the treatment period at Day 28.
• Mite eradication: The average mites/lash showed statistically significant improvement from baseline to Day 14 and had a 10-fold improvement from baseline by the end of the treatment period at Day 28.
• Safety: No treatment-related adverse events were reported and there were no clinically significant changes in visual acuity, intraocular pressure and slit-lamp biomicroscopy findings including in corneal staining.
Says Tarsus CEO Bobak Azamian, MD, PhD: “These results are the beginning of a strong, consistent data set we are generating with TP-03 to treat the underlying cause of demodex blepharitis and other conditions.”
Looking ahead
Tarsus planned to release results of the Jupiter Study, a Phase 2b Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of TP-03 for the Treatment of Demodex Blepharitis, at the American Optometric Association’s (AOA) annual meeting, this year held virtually.
In addition, the company plans to file an IND for TP-03 to treat demodex blepharitis and begin a Phase 3 trial later this year. Its clinical pipeline also includes studies in meibomian gland disease (MGD) and rosacea.

Newsletter
Want more insights like this? Subscribe to Optometry Times and get clinical pearls and practice tips delivered straight to your inbox.