- March digital edition 2023
- Volume 15
- Issue 03
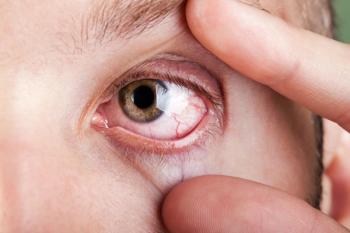
Management of chronic allergic eye disease
Treatment should be adjusted based on disease severity.
Ocular allergies, like systemic allergies, can vary in severity, and medical treatment should be adjusted accordingly.
First-line options such as allergen avoidance, cool compresses, preservative-free lubricating eye drops, and over-the-counter medications like mast-cell stabilizers, antihistamines, and combination eye drops are a reasonable approach to seasonal or intermittent allergic conjunctivitis that responds well to management.1
More severe and recalcitrant cases may require a topical corticosteroid to reduce ocular surface inflammation and symptoms. Although corticosteroids are effective, their long-term use requires caution due to such possible complications as elevated IOP, cataract formation, and increased risk of microbial infection.2
Immunomodulating medications like cyclosporine A and tacrolimus may be used in the long-term for severe and recurrent cases of such allergic eye disease (AED) as vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC).3 In June 2021, the FDA approved cyclosporine 0.1% (Verkazia; Santen Pharmaceutical) for VKC in adolescents and adults. Protopic (tacrolimus) is FDA approved in the second line for atopic dermatitis. Protopic ointment 0.03% is used in patients aged 2 to 15, and both Protopic ointment 0.03% and 0.1% can be used in those 16 years and older.4 It is important to keep the ointment on the periocular skin and caution patients to avoid getting it in the eyes.
References
Carr W, Schaeffer J, Donnenfeld E. Treating allergic conjunctivitis: a once-daily medication that provides 24-hour symptom relief. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2016;7(2):107-114. doi:10.2500/ar.2016.7.0158
Liu S, Saldanha IJ, Abraham AG, et al. Topical corticosteroids for dry eye. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;10(10):CD015070. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015070.pub2
Erdinest N, Solomon A. Topical immunomodulators in the management of allergic eye diseases. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;14(5):457-463. doi:10.1097/ACI.0000000000000089
FDA. Medication Guide: Protopic. 2006.
Articles in this issue
over 2 years ago
New topical therapies for dry eye diseasealmost 3 years ago
Diagnosing and treating optic nerve head drusenalmost 3 years ago
OCT biomarkers associated with advanced age-related macular degenerationalmost 3 years ago
Educating patients on refractive surgery optionsalmost 3 years ago
My practice journeyalmost 3 years ago
Artificial tear ingredients that mimic the real thingalmost 3 years ago
Supporting glaucoma patients beyond the exam roomalmost 3 years ago
Breaking into lens techNewsletter
Want more insights like this? Subscribe to Optometry Times and get clinical pearls and practice tips delivered straight to your inbox.